
Steroids and other performance and image-enhancing drugs (PIEDs) have long been associated with elite sportspeople desperate for an edge. PIEDs are used by people of all skill levels and ages, whether they want to boost their sporting performance or simply build muscle mass.
Among the most notorious cases was champion cyclist Lance Armstrong, who was stripped of seven Tour de France wins after admitting he took EPO (erythropoietin), which regulates red blood cell production.
PIED use is not common and in some cases, steroids are used legitimately to treat medical conditions such as osteoporosis. But if used privately and without professional supervision they can have health implications.
Steroids may be injected intramuscularly, taken orally or rubbed on the skin as a cream. Two per cent of Australian high-school students aged 12 to 17 say they have used steroids without a doctor’s prescription, with boys (2.4 per cent) slightly more likely than girls (1.5 per cent) to have tried them.
Among the 1 per cent of students who tried steroids in the year before the 2011 survey, use was infrequent. Read more
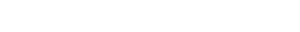


 Hallucinogens, such as LSD, were popular with young people during the 1960s and 1970s “flower power” era. While many more drugs have been developed since, LSD is still available in Australia.
Hallucinogens, such as LSD, were popular with young people during the 1960s and 1970s “flower power” era. While many more drugs have been developed since, LSD is still available in Australia.


 By Cheryl Critchley
By Cheryl Critchley

 By Cheryl Critchley
By Cheryl Critchley
